WPS Focus: Display of Pesticide Safety, Application and Hazard Information
Since it was implemented in 1992, the Worker Protection Standard (WPS) has required that growers who apply pesticides referencing the WPS in 40 CFR Part 170 to agricultural plants record information about the pesticides applied and display it in a “Central Location” where the information could be readily seen and read by workers. It has also required the display of basic pesticide safety information advising workers on how to protect themselves from pesticides that they might contact during their work on an agricultural establishment. The 2015 revised Worker Protection Standard continues to require the display of pesticide safety and application information with some changes.
One significant change is that growers will have to display hazard information, specifically safety data sheets (SDS), for pesticides applied along with the pesticide application information. The pesticide application information will now also include the start and end times of application and the crop or site treated. Listed below is the application and hazard information that must be displayed no later than 24 hours after the end of a pesticide application:
- A copy of the Safety Data Sheet (SDS) for each pesticide applied;
- The name(s), EPA Registration number(s), and active ingredient(s) of each pesticide applied;
- The crop or site treated and the location and description of the treated area;
- The date(s) and times the application started and ended.
- The duration of the applicable labeling-specified restricted-entry interval for that application.
Another significant change relates to the retention of the above information. Under the original and revised WPS, this information must be displayed for 30 days from the end of the last applicable restricted entry interval for an application. In the past, WPS did not require it to be retained once the 30 days expired. Beginning in 2017, employers will still have to display the information for 30 days but will also have to retain it for 2 years after the restricted-entry interval applicable to a pesticide application expires. Note that the 30 day display is required when workers or handlers are on the establishment during that period. The information does not have to be displayed the full 30 days if no workers or handlers are present. It would still have to be retained for 2 years if it was required to be displayed at the central location.
The revised WPS no longer specifically references the “Central Location” but still requires the display to be at a place where workers and handlers are likely to pass by or congregate and where it can be readily seen and read. For the purposes of this article, the term “Central Location” will continue to refer to the site designated by the employer for the display of application and hazard information. The employer must make sure that all of the displayed information required by WPS is legible and accessible to workers on the establishment at all times during normal work hours.
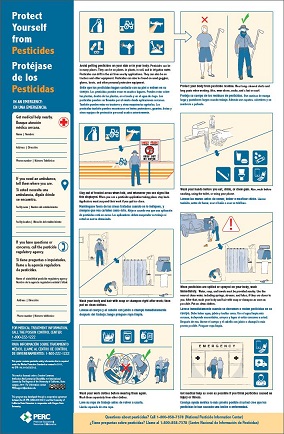
- Avoid getting on the skin or into the body any pesticides that may be on or in plants, soil, irrigation water, tractors, and other equipment, on used personal protective equipment, or drifting from nearby applications.
- Wash before eating, drinking, using chewing gum or tobacco, or using the toilet.
- Wear work clothing that protects the body from pesticide residues (long- sleeved shirts, long pants, shoes and socks, and a hat or scarf).
- Wash or shower with soap and water, shampoo hair, and put on clean clothes after work.
- Wash work clothes separately from other clothes before wearing them again.
- If pesticides are spilled or sprayed on the body use decontamination supplies to wash immediately, or rinse off in the nearest clean water, including springs, streams, lakes or other sources if more readily available than decontamination supplies, and as soon as possible, wash or shower with soap and water, shampoo hair, and change into clean clothes.
- Follow directions about keeping out of treated areas and application exclusion zones.
- Instructions to employees to seek medical attention as soon as possible if they believe they have been poisoned, injured or made ill by pesticides.
- The name, address, and telephone number of a nearby operating medical care facility capable of providing emergency medical treatment. This information must be clearly identified as emergency medical contact information on the display.
- The name, address and telephone number of the State or Tribal pesticide regulatory agency.
Revised posters containing the new content have been developed by the Pesticide Educational Resources Collaborative (PERC) in collaboration with the US EPA. Penn State has also developed an EPA approved poster. These posters are now available for agricultural employers to use. The PERC version of the poster is available for download or order from the PERC website. Information about obtaining copies of the poster appears at the bottom of this page. Employers can also create their own display in other formats so long as all of the required new content is included.
As part of the pesticide safety information posting, the employer must provide information about nearby operating medical care facility capable of providing emergency medical treatment. This information is to be clearly identified in the display as emergency medical contact information. It must include the name, address and telephone number of the identified establishment. The PERC and Penn State versions of the poster have sections for the emergency medical care facility which the agricultural employer can fill out.
Unlike the pesticide application and hazard information, the pesticide safety information must now also be displayed at other locations on the establishment. In addition to the “Central Location” it must be displayed where decontamination supplies are provided at permanent sites, like bathrooms. The pesticide safety information must also be provided at temporary locations if the decontamination supplies are provided in quantities to meet the requirements for 11 or more workers.
Although the pesticide application and hazard information may be removed from display after 30 days, there are provisions for requests for copies or access to the information during the 2 year retention period. WPS has specific provisions permitting current and former employees, treating medical personnel and designated representatives to request access to or copies of pesticide application and hazard information. These provisions will not be discussed in this article but are found in 40 CFR §§170.311(b)(7), 170.311(b)(8) & 170.311(b)(9). Under 40 CFR §170.309(m), agricultural employers would also have to provide any records to authorized representatives of the state or federal government upon request for inspection or copying.
Additional information on the rule is available on the Agricultural Worker Protection Standard (WPS) page of the EPA's website. You can visit the site by clicking here.
If you have additional questions about the new training requirements feel free to contact Marlene Larios, the Coordinator for the Worker Protection Standard. Ms. Larios can be reached by phone at (804) 786-8934 or by email at marlene.larios@vdacs.virginia.gov.
Ordering Copies of Worker Protection Standard Materials
A copy of the Pesticide Safety Poster can be downloaded for free from the PERC website for printing locally. You should have a printer capable of printing on 11" X 17" (tabloid) size paper or take it to a commercial printer. Click here to download a printable copy of the poster.
While a number of WPS resources are available online, hardcopies of the pesticide safety posters and Respiratory Protection Guide can be ordered via the National Pesticide Safety Education Center (NPSEC). To learn more about NPSEC click here.
- To order pesticide safety posters click here.
- To order a copy of the WPS Respiratory Protection Guide click here.